Sickle cell disease is called diseases that are red blood cell disorder and inherit the person through the gene. It is a genetic disorder resulting from abnormal genes. It is an inherited disease which means that this disease is caused by genes from parents to their children. It is not contagious or infectious and is not transmitted by an infection from person to person.
Sickle cell diseases in India are mainly found in Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala, Karnataka, and some north-eastern states.
How is sickle cell disease?
People with sickle cell disease have abnormal hemoglobin in red blood cells called sickle hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body.
In which sickle cell disease is found, two abnormal hemoglobin genes are observed that come from each parent. In all forms of sickle cell disease, at least one in two abnormal genes is caused by normalization in the body of a person.
When a person has two hemoglobin S (sickle hemoglobin) genes, hemoglobin SS, the disease is called sickle cell anemia. It is the most common and often the most serious type of sickle cell disease. Hemoglobin SC disease and hemoglobin SB thalassemia Hemoglobin SC disease and hemoglobin Sβ thalassemia are two other forms of sickle cell disease.
It is important to note that every time this couple has a child, the child with sickle cell disease is likely to be the same. In other words, if the first congenital child has sickle cell disease, there is still a 25 percent chance that the second child will also have a disease. Both boys and girls can have this disease.
If a person wants to know if he carries a sickle hemoglobin gene, a blood test can detect it.
Other names for sickle cell anemia
- HBS Disease
- Hemoglobin S Disease
- Hemoglobin SS Disease
- Sickle cell disease (a wide term that involves sickle cell anemia)
- Sickle cell disorder (a wide group of conditions that include sickle cell anemia)
The effects of sickle cell anemia?
Cells in the tissue require a stable supply of oxygen to work well. Generally, the hemoglobin present in red blood cells takes oxygen from the lungs and carries all the tissues of the body.
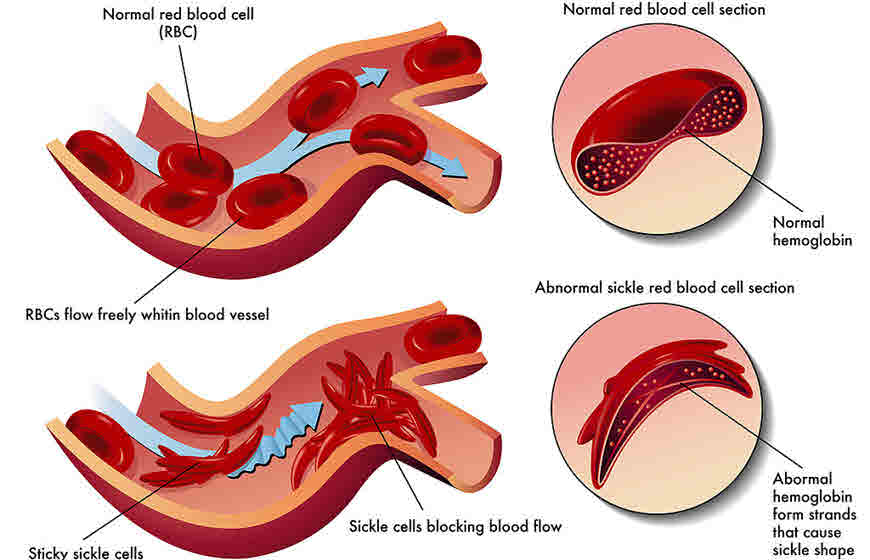
The usual hemoglobins found in red blood cells are the size of the disc and look like a doughnut without a hole. This shape makes the cells flexible so that they can move through large and small blood vessels to deliver oxygen. But sickle hemoglobin is not like normal hemoglobin. It is a crescent or sickle shape. With a shape like a rod, it gets stuck in blood vessels which can stop the supply of oxygen.
Lack of oxygen in the tissue leads to sudden severe pain. These pains are often sudden and the victim should go to the hospital for its effective treatment. Lack of oxygen can also cause damage to organs. The entire body parts, including spline, brain, eyes, liver, kidney, penis, joints, can be damaged by the supply of less oxygen.
Sickle cells can not easily change the shape, so they break down very quickly. Normal red blood cells survive from about 90 to 120 days, but sickle cells only last for 10 to 20 days.
The body always keeps changing old red blood cells new. But in sickle cell disease, cells are being destroyed rapidly in the body and this causes the build and damage balance not to remain. Because of this, the number of red blood cells is usually reduced by normal and this form of anemia is called sickle cell anemia and in this case, the person produces less energy than the energy needed for the body.
Symptoms of sickle cell disease
If a person has sickle cell disease, it is by birth but most infants have no problem with the disease unless they are about 5 or 6 months old.
Some children may see the following symptoms:
- Painful swelling of the hand and legs called dactylitis
- Fatigue or nervousness with anemia
- The yellow color of the skin, jaundice
- Prolonged pain in the body
- Mild to moderate anemia occurs several times, however, they may have severe anemia.
Major complications of sickle cell disease
Acute Pain (Sickle Cell or Vaso-Occlusive) Crisis Acute Pain (Sickle Cell or Vaso-occlusive) Crisis.
Episodes of pain can occur without warning. This happens when sickle cells block blood flow and reduce the amount of oxygen. People tell this pain as fast, intense, stabbing, or throbbing. This pain can be more than post-surgical pain or childbirth.
Pain can occur almost anywhere in the body and in more than one place at a time. But pain is often seen in:
- Lower back
- Foot and hand
- Stomach and chest
Infection
Spleen is important for protection against certain types of germs. Sickle cells can damage the spleen and weaken or destroy its function.
The damage to the spleen increases the risk of serious bacterial infections in the body. Some infections that may occur are:
- Pneumococcus
- Hemophilus influenza Type B
- Meningococcus
- Salmonella
- Staphylococcus
- chlamydia
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Blood infection (septicemia)
- Lung infection (pneumonia)
- Infection of the covering of the brain and spinal cord infection of the covering of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis)
- Bone infection (osteomyelitis)
- Acute Chest Syndrome
Blockage in the blood vessels of the lungs is a dangerous condition in which the areas of lung tissue are damaged. This condition is very serious and should be treated immediately in the hospital.
Symptoms may include:
- Chest pain
- Fever
- Lack of breath
- Rapid breathing
- Cough
- Brain Complications
A stroke occurs when the blood flow blocks a part of the brain. When this happens, brain cells can be damaged. This is a very dangerous situation.
Symptoms depend on which parts of the brain are affected. Symptoms of a stroke may include:
- The weakness of one hand or foot on one side of the body
- Difficulty in speaking, walking, or understanding
- Terrible headache
- Eye Problems Eye Problems
Sickle cell disease can injure blood vessels in the eyes. The most common site of damage is the retina, where blood vessels may increase more, be blocked, or bleeding.
The retina may be different so that light can be made.
Kidney Problems Related to Kidney Problems
Renal red blood cells are sensitive to the effects of roads. In sickle disease, the kidneys have difficulty concentrating urine. This often requires urination.
Other problems it often begins in childhood may include:
- Blood in urine
- Kidney disease
- Protein in urine
- Prolonged Stress
Priapism in Penis
Men suffering from this disease sometimes have prolonged, painful erections. If erections remain for a longer period of time, the priapism penis can cause permanent damage and can cause impotence.
Gallstones
When red cells are hemolyzed, they hatch hemoglobin. Hemoglobin breaks down into a substance called bilirubin can form bilirubin stones that get stuck in the gallbladder.
Gallstone does not have symptoms for many years. When symptoms develop, it may include:
- Right-sided upper abdominal pain
- to feel sick
- Vomiting
- If problems persist or recurrence occurs, a person may need surgery to remove the gallbladder.
The sickle disease affects every part of the body.
Treatment of sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease is a life-long disease the severity of the disease varies from person to person. No treatment of sickle cell anemia is available.
Currently, available for it in developed countries, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only treatment for SCD. Unfortunately, most people with sickle cell disease are either very old for transplantation or do not have relatives who may have their genetic match right. A successful transplant requires a well-matched donor.
There are effective treatments that can reduce symptoms and advance life. Early diagnosis and regular medical care also contribute to improved improvements to prevent complications.
The term sickle cell disease includes a group of inherited red blood cell disorders.
In this condition, there is abnormal hemoglobin, called hemoglobin S or sickle hemoglobin, is found in the red blood cells. Sickle cell disease is an inherited disease that goes form the parents to their children through genes. Sickle hemoglobin is not like normal hemoglobin. It can form stiff rods within the red cell, changing it into a crescent, or sickle shape.
Sickle-shaped cells are not flexible and can stick to vessel walls, causing a blockage that slows or stops the flow of blood. When this happens, oxygen can’t reach nearby tissues. The red cell sickling and poor oxygen delivery can also cause organ damage. Over a lifetime, SCD can harm a person’s spleen, brain, eyes, lungs, liver, heart, kidneys, penis, joints, bones, or skin.
Sickle cell disease is a life-long illness. The severity of the disease varies widely from person to person. There is no cure available for the disease. The only treatment is given depending on the sign and symptoms.