Prostate gland small gland which lies between penis and urinary bladder. Its job is to make a fluid that combines with sperm to produce semen. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in medical language.
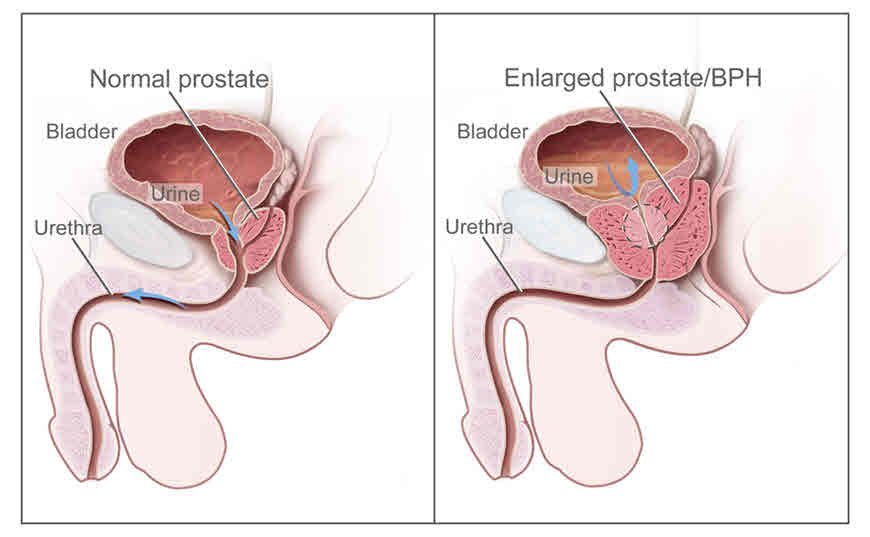
Benign prostate enlargement (BPE) increases the size of the prostate. Due to its increased size, problems of urination arises. BPE is common in men over 40 years of age. It is not cancerous and is generally not a serious health hazard.
What is prostate
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The main function of the prostate is to make a fluid that goes into the semen. The prostate fluid is essential for fertility. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra on the neck of the bladder. The prostate consists of two or more parts and it is under the urinary bladder and in front of the anus.
Cause of prostate enlargement
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not yet understood. Some researchers believe that it may be due to factors related to aging and testicles. Male hormones testosterone is produced in excess in males, and estrogen female hormones in small amounts. The amount of active testosterone in the blood decreases with age, and estrogen is increased in proportion. Scientific studies have suggested that a high proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth. Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Dihydrotestosterone, which is a male hormone, plays a role in the growth and development of the prostate. Some research has indicated that with the drop in blood testosterone levels, higher levels of DHT are produced and mobilized in the prostate. The accumulation of DHT can stimulate prostate cells to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop prostatic hyperplasia.
The prostate gland is found in males and it helps to make semen which contains sperm. The prostate surrounds the urine carrying tube. The prostate gets enlarged with aging. An enlarged prostate is also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called benign enlargement of the prostate (BEP or BPE) or benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction. It is an enlarged prostate gland.
An enlarged prostate presses against and pinches the urethra and the bladder wall also becomes thicker. Eventually, the bladder may weaken and lose the ability to empty completely causing some urine retention. The narrowing of the urethra and urinary retention are responsible for the problems associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, What is BPH?
Benign hyperplasia of the prostate or BPH is the abnormal growth of the prostate or prostate with age. The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system. It is situated under the bladder. The urinary tube passes through it.
The prostate gland grows with age. Due to its increased pressure on the urinary tube and it shrinks. Because of this, the bladder is not completely emptied and there is always some urine or urine left in it.
Urine accumulation in the body leads to urine retention and urinary problems such as:
- Willingness to urinate frequently, especially at night
- Inability to pass urine properly, weakening of the edge, closure again, drop of urine
- Urination, etc., even after passing urine.
What can cause benign prostate enlargement?
The cause of prostate enlargement is unknown, but it is believed that it may be caused by hormonal changes occurring in the body upon aging.
The balance of hormones in the body changes with age, which can make the prostate gland enlarge.
Which men are more likely to have prostatic hyperplasia?
The following factors are more likely to cause prostate enlargement:
- Over 40 years old
- Family history
- Obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes
- lack of exercise
- Erectile dysfunction
What are the symptoms of benign prostate enlargement or prostatic / prostate hypertrophy?
The prostate is a small gland found in men that lies between the penis and the bladder in the pelvis. If the prostate enlarges, it can put pressure on the bladder and urethra (the tube through which urine passes). This causes symptoms of urination. This can cause the following problems:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Frequent urination – eight or more times a day
- Difficulty emptying the bladder completely
- Inability to delay urination
- Urine retention
- No urination
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Stopping urination
- Urination infection
- Pain after ejaculation or during urination
- Unusual color or smell in urine
In some men, the symptoms are very rare and do not require treatment; in others, it may be more and more troublesome.
Test for diagnosis of prostate enlargement
What tests are done for benign prostate enlargement?
You will need some tests to find out if your prostate gland has grown.
- Physical exam
- Digital rectal exam
- Urine test
- Blood test
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test
- Neurological examination
- Urinary flow test
- Postvoid residual volume test
- 24-hour voiding diary
Some other tests that can be done:
- Transrectal ultrasound
- Prostate biopsy
- Urodynamic and muscular studies
- Cystoscopy
- Intravenous pilogram or CT urogram Intravenous pyelogram or CT urogram
What are the complications of prostate enlargement?
- Urinary tract infections
- Acute urinary retention
- Blood in urine
- Bladder damage
- Kidney damage
- Bladder stones
Symptoms of acute urinary retention include severe abdominal pain, bladder inflammation, and sudden urination/stoppage.
What is the treatment in allopathy for prostate enlargement?
Treatment options for prostate enlargement may include
- Lifestyle changes
- Prescription drugs
- Surgery
Medications are the most common treatment for mild to moderate symptoms of prostate enlargement. Options include:
The medicines
Alpha-Blockers
These drugs relax the muscles and fibers of the bladder neck in the prostate, making it easier to urinate. Alpha blockers alfuzosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, silodosin usually work early in men with relatively small prostates. Side effects include dizziness and retrograde ejaculation (retrograde ejaculation).
- alfuzosin (Uroxatral)
- doxazosin (Cardura)
- silodosin (Rapaflo)
- tamsulosin (Flomax)
- terazosin (Hytrin)
5- alpha-reductase inhibitors
These drugs prevent your prostate from hormonal changes that cause prostate enlargement. These medicines – including finasteride and dutasteride finasteride dutasteride. It may take up to six months to take effect. Side effects include retrograde ejaculation (retrograde ejaculation).
- dutasteride (Avodart)
- finasteride (Proscar)
Combination drug treatment Combination drug therapy
- It consists of an alpha blocker and a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor given at the same time if the drug alone is not effective.
- finasteride and doxazosin
- dutasteride and tamsulosin (Jalyn), a combination of both medications that is available in a single tablet
- alpha-blockers and antimuscarinics
Surgery
In addition to medicine, surgery is also an option.
Transurethral resection of prostate Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
The surgeon inserts a light scope into the urethra to remove the external posture of the prostate.
After TURP you will need a catheter to temporarily empty your bladder and you will only be able to do the light activity until healing is complete.
Transurethral incision of prostate Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP)
Surgeons insert a special electrode through the urethra into the prostate area. Microwave energy emitted from the electrode destroys the inner part of the enlarged prostate gland. This causes the prostate to shrink and ease urine flow.
Transurethral needle ablation Transurethral needle ablation (TUNA)
In this outpatient procedure, the needle is inserted into the urethra by inserting the scope into the urethra, thereby transmitting radio waves and destroying the enlarged portion of the prostate gland. This method can only partially alleviate your symptoms.
Laser Therapy Laser Therapy
The laser destroys an enlarged part of the prostate gland. Laser therapy usually provides immediate relief from symptoms and has a lower risk of side effects than nonlaser surgery.
Prostate Medications Side Effects
Medications used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia have side effects that can sometimes be severe. Men should talk to the doctor about possible side effects before taking prescribed medicines for the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia.
The doctor should immediately contact or receive emergency medical care if you experience the following side effects:
- Hives hives
- Rash rash
- Itching
- Trouble taking breath shortness of breath
- Rapid, or irregular heartbeat rapid, pounding, or irregular heartbeat
- Prolonged erection painful erection of the penis that lasts for hours
- Swelling of the eyes, face, tongue, lips, throat, hands, hands, feet, ankles or lower legs swelling of the eyes, face, tongue, lips, throat, arms, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Chest pain
- Sudden dizziness or faint dizziness or fainting when standing up suddenly
- Sudden low vision sudden decrease or loss of vision
- Blurred vision blurred vision
- Sudden hearing difficulty Sudden decrease or loss of hearing
- Chest pain, dizziness or nausea during sexual activity chest pain, dizziness, or nausea during sexual activity
Surgery side effects
Complications after surgery may include:
- Urination problems
- Urinary incontinence
- Bleeding and blood clots
- Infection
- Scar tissue
- Sexual dysfunction
- Frequent urinary retention and UTIs are recurring problems such as urinary retention and UTIs
- Infection
- Stop urinating
- Blood in urine
- Having sexual dysfunction
- Need to undergo surgery several times
Ayurvedic and homeopathic medicines for benign prostatic hyperplasia
As the prostate increases, problems related to urination become very high. Urine drops by drop and does not form an edge. There is a need to urinate several times during the night, which causes sleep disturbances. In such a situation, when a person takes allopathic medicines, then the problems of urination may be relaxed but many other problems start. The effect of the drug causes sleepiness and inability to sleep can lead to other health problems. Consumption of medicines can cause itching, skin rashes, poor hearing, dizziness, etc.
If the person is considering getting surgery, then he should make this decision very carefully. As much information as possible should be gathered about it. It should be reviewed by the people and the doctor should clear your douche. One should assume that this is not a very easy surgery. Even after getting it done, he will not get relief from urinary infections and other urinary problems. After surgery, he may have to consume many pain relievers and antibiotics for 2-3 weeks. It may also happen that after some time he has to undergo this surgery again.
There are many medicines in Ayurveda and homeopathy for prostrate treatment. Homeopathic medicines for this disease benefit more than Ayurvedic medicines.
Before starting allopathic medicine, definitely try taking an Ayurvedic or homeopathic medicine.
Ayurvedic and homeopathic medicines are beneficial in urination symptoms.
Ayurvedic Medicines
- Chandraprabha Vati Chandrapabha Vati
- Goksuradi Guggugu Gokshuradi Guggulu
- Hog Purnarnava
- Prostige Charak Charak Prosteez Tablets
- Prostacare Himalaya Himalaya ProstaCare
- Homplasia Himalaya Himalaya Himplasia
- Prosta Baidyanath Baidyanath Prostaid
Homeopathic Medicines
- Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens)
- Sabal Serrulata
- SBL Prostonum drops
- Proscenat ADEL 21
- RECKEWEG R 25
- SCHWABE Sabal cast
Lifestyle and Home Remedies in Prostate Enlargement
- Take limited beverages in the evening. Do not take water or fluids after 7-8 pm in the evening.
- Caffeine and alcohol can increase urine production, do not consume them.
- Avoid intake of decongestants and antihistamines. It tightens the urethra, causing difficulty in urination.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Reduce salt intake.
- Do not take heavy food to digest.
- Drink turmeric milk.
- Drink plenty of water so that there is no burning sensation in the urine.
- Do not stay in low temperatures. This causes frequent urination.
- Drink Amla juice.
- Take a spoonful of pumpkin seeds.
- Do not let yourself be constipated.
- Be active